Cartesian diver that floats when force is applied
Let's take a look!
What type of experiment is this?
Experimental procedure and explanation:
- An ordinary " cartesian diver " sinks when the container is pushed and floats up when the force is relaxed. The floater in this video is contrasting: it floats up when force is applied and sinks when force is relaxed.
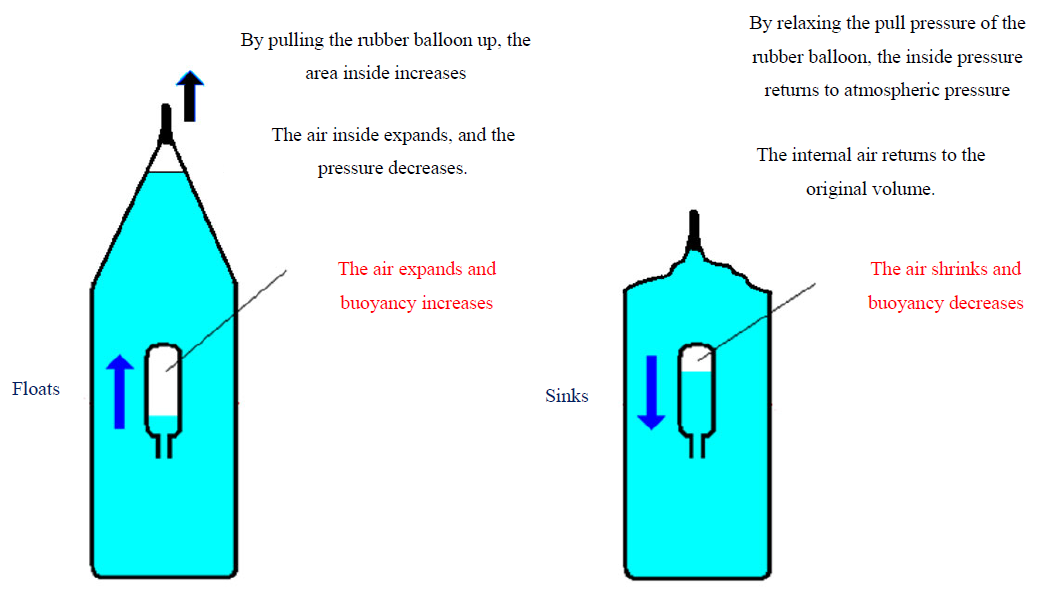
- We can adjust amount of water inside the floater so that it sinks slightly into the water. We place it in a jug filled with water, cover the mouth with a rubber balloon (45 cm in size on this occasion, cut off the tip), and fasten it tightly with a thick rubber band.
- Pulling the tip of the rubber balloon upward increases the volume inside and decreases the water and air pressure inside. As the volume of air in the floater increases, the buoyancy force acting on the floater increases, and the floater floats up.
- At this time, the internal pressure is less than atmospheric pressure. A pressure below the atmospheric pressure is referred to as "negative pressure.”
- When the pulling force applied to the rubber balloon is relaxed, the water and air pressure inside increases and it returns to atmospheric pressure again. Because the volume of air in the flotation device is reduced, the buoyancy becomes smaller and the floater sinks.
- The principle of the flotation at this time is the same as in Cartesian Diver that Floats when Squeezed.
- This experimental video was produced with the support of JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research 18K03956.
| [Keywords] | Buoyancy, Cartesian diver, negative pressure |
| [Related items] | Cartesian diver, Cartesian Diver that Floats when Squeezed. |
| [Reference] | Ryozo Ishiwata, "The Wonder of Flow," Kodansha Blue Backs, p. 34-37, p. 42-47 Ryozo Ishiwata, "Illustrated Fluid Dynamics Trivia", Natsume Publishing, P14-15, P34-35 |
Last Update:1.31.2025

