Measure Bottle Volume
Let's take a look!
What type of experiment is this?
Experimental procedure and explanation:
- Let’s use the principle of buoyancy to measure the volume of a bottle.
- Place a container filled with water on the scale and reset the display to zero.
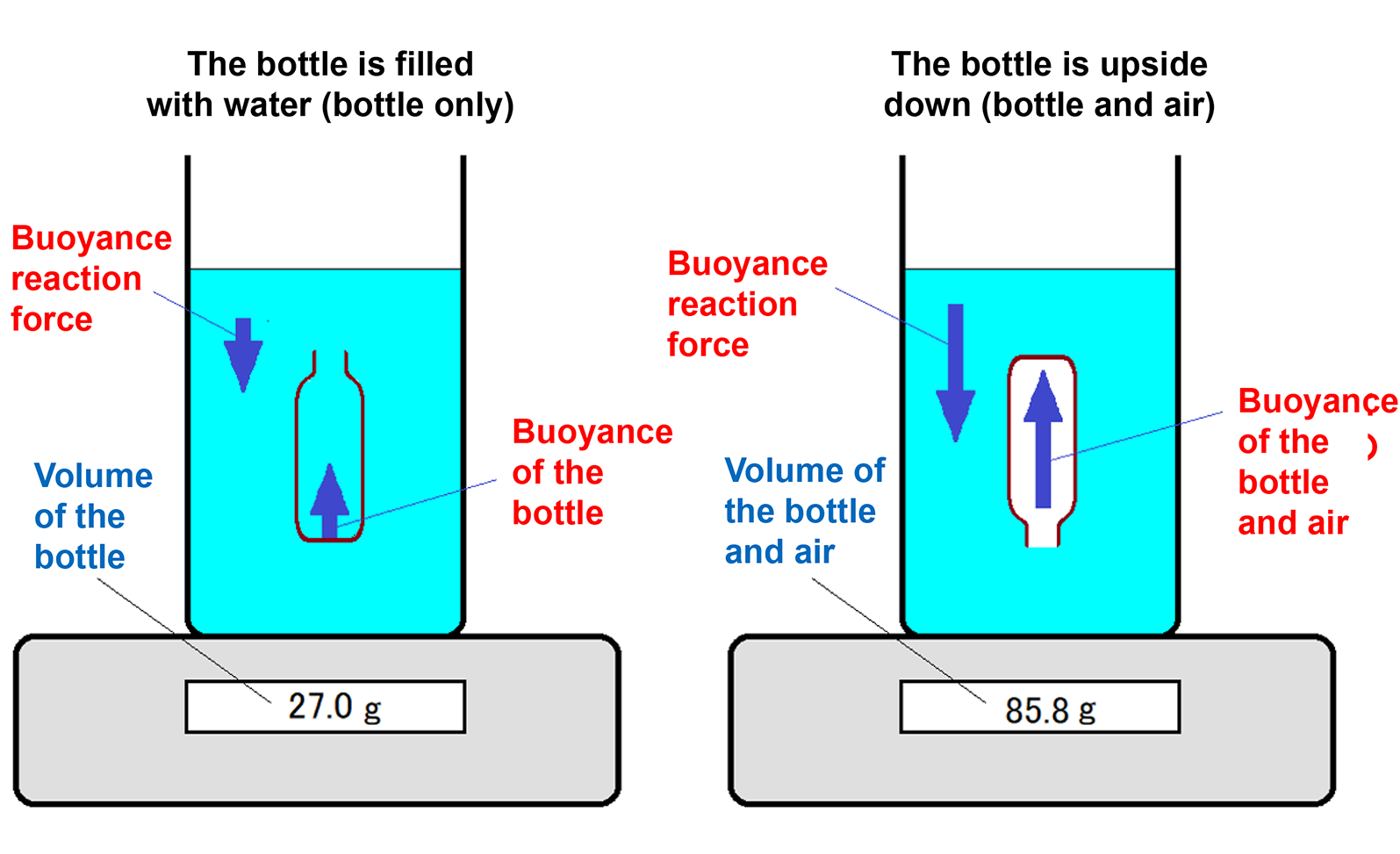
- Submerge the bottle upright in the water and fill it completely.
- Using tongs, lift the bottle slightly so it is fully submerged without touching the container’s bottom or rising above the water surface. Ensure no air bubbles cling to the bottle.
- Read the scale display; this value corresponds to the weight of the displaced water, which equals the bottle’s volume (glass part) in cubic centimeters (cm3) according to Archimedes’ principle:
- (displayed weight [g]) = (volume of water [cm3]) = (volume of object [cm3]).
- Next, remove the bottle from the water and pour the water inside back into the container. Place the bottle upside down in the water. Read the value displayed on the scale; this represents the combined volume of the bottle and the air inside it. Subtract the volume of the bottle alone (measured earlier) from this value to find the volume (capacity) of the hollow space inside the bottle.
- For example, in the video, the bottle alone weighs 27.0 g, and the bottle with air inside weighs 85.8 g. Therefore, the bottle’s capacity is 85.8 − 27.0 = 58.8 cm3.
- This video was produced with the support of the JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18K03956).
| [Keywords] | Buoyancy |
| [Related items] | |
| [References] | Ryozo Ishiwata and Mitsumasa Nemoto, “The Wonder of Flow,” Kodansha Bluebacks, pp. 48–51. |
Last Update: 2021.6.1

