A Cartesian Diver that Floats when the Bottle Is Lifted
Let's take a look!
What type of experiment is this?
Experimental procedure and explanation:
- A Cartesian diver sinks inside a plastic bottle under normal conditions.
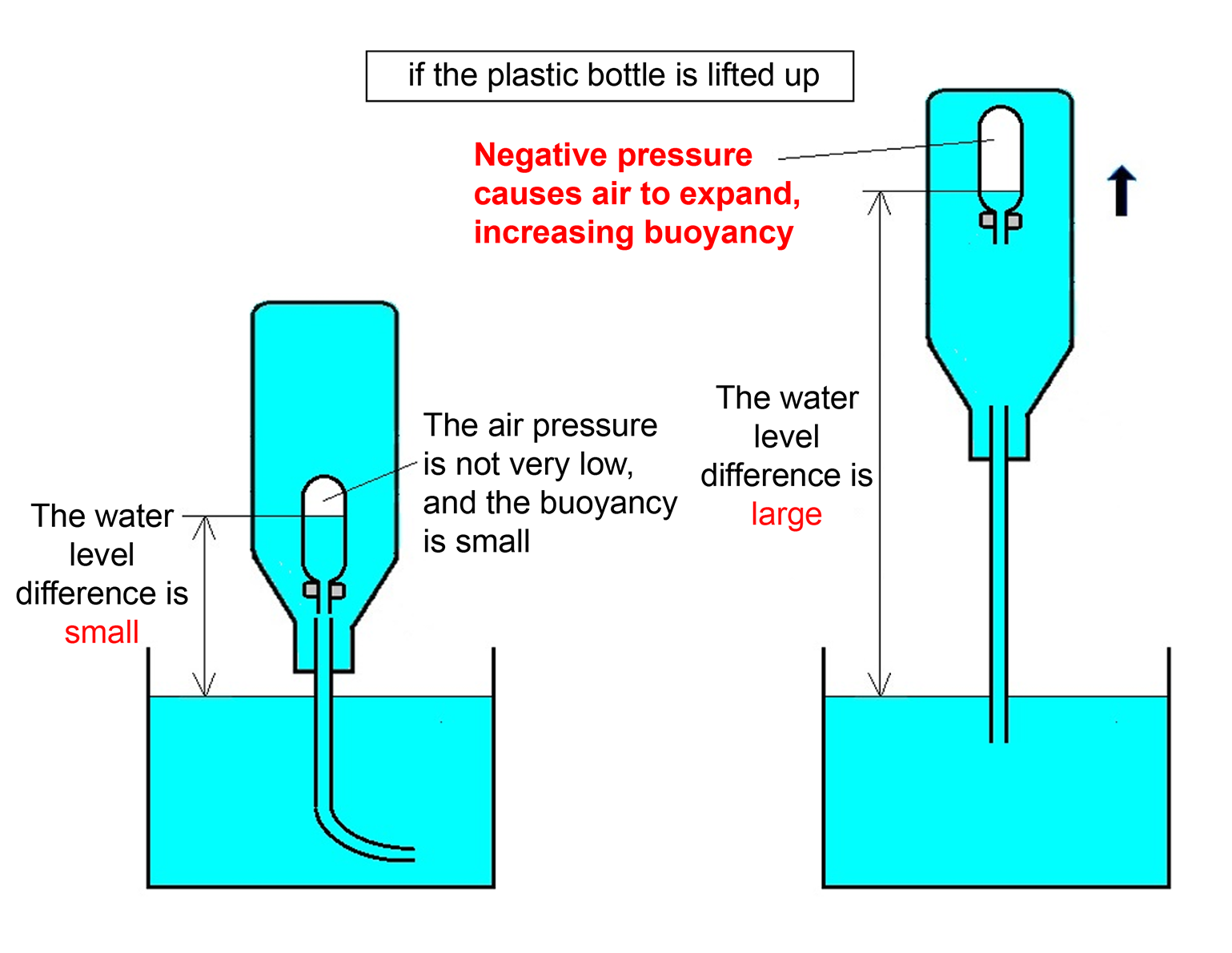
- When the plastic bottle is lifted, the Cartesian diver begins to float upward.
- When the plastic bottle is lowered, the Cartesian diver sinks again. Why does this happen?
- A plastic hose is attached to the cap of the bottle, connecting it to a water tank below. When the bottle is lifted, the water level inside rises above the water level in the tank. This creates a pressure inside the bottle that is lower than atmospheric pressure—known as negative pressure. As a result, the air inside the Cartesian diver expands. This increase in volume decreases the diver’s overall density and increases the buoyant force acting on it, causing it to float upward.
- Conversely, when the plastic bottle is lowered, the pressure inside the bottle increases. This causes the volume of air inside the Cartesian diver to decrease. As the volume shrinks, the diver’s buoyancy decreases, and it sinks.
- Tip 1: Use a plastic bottle that does not dent easily. In this video, the experiment was difficult because the bottle became dented.
- Tip 2: Use a Cartesian diver that floats and sinks easily (such as the one shown in this experiment Cartesian Diver), and adjust the amount of water inside so that it sinks slightly. This makes it easier to perform the experiment successfully.
- This video was produced with the support of the JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (18K03956).
| [Keywords] | Depth and pressure, buoyancy, Cartesian diver, negative pressure |
| [Related items] | Cartesian Diver, Turn a plastic bottle with a hose upside down, Cartesian diver that floats when force is applied, Cartesian Diver that Floats When Squeezed |
| [References] | Ryozo Ishiwata and Mitsumasa Nemoto, “The Wonder of Flow,” Kodansha Bluebacks, pp. 38–47. Ryozo Ishiwata, “Illustrated Fluid Dynamics Trivia,” Natsume Publishing, pp. 18–19. |
Last Update:2022.6.1

