Newsletter 2014.1 Index
Theme : "The Conference of Fluid Engineering Division"
| Back | |
An attempt to measure wall shear stress fluctuation in a turbulent wall jet
Takuya SAWADA  Kouji NAGATA  Mitsuhiro SHIKIDA  Yasumasa ITO Nagoya University |
Abstract
The objective of this study is to establish a technique for accurately measuring the wall shear stress in turbulent flows using a micro-fabricated hot-film sensor. In this study, micro-scale hot-film sensor, “Silicon hot-film sensor”, to measure wall shear stress fluctuation is fabricated. Silicon hot-film sensor has a 1 mm-thick silicon wafer, which is realized via an alkali etching process, as its substrate to reduce heat capacity of the substrate, whereas previous hot-film sensor has a 25 mm-thick polyimide film and 0.5 mm-thick silicone rubber film as the substrate. Calibration result in a turbulent wall jet by means of the Preston tube shows that the sensor can measure the time-averaged wall shear stress as expected. In addition, the result of the frequency response test with the sinusoidal wave heat current shows that the frequency response of the Silicon hot-film sensor is 1,000 Hz, whereas that of the previous hot-film sensor is 7 Hz.
Key words
Wall shear stress fluctuation, Turbulent wall jet, Micro-fabricated sensor, Hot-film sensor
Figures
 |
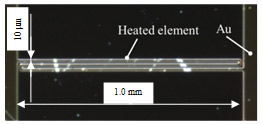 |
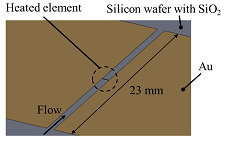
| Fig.1 Schematic view and photograph of the heated element of Silicon hot-film sensor |
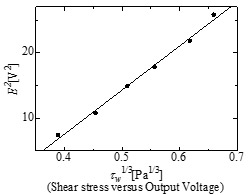 |
| Fig.2 Calibration result of the Silicon hot-film sensor in a turbulent wall jet |
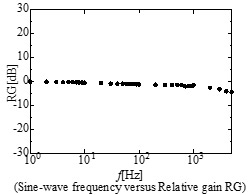 |
| Fig.3 Frequency response of the Silicon hot-film sensor |




