Newsletter 2016.11 Index
Theme : "Mechanical Engineering Congress, 2016 Japan (MECJ-16)"
|
Energy transfer and drag reduction in the fluid diluted with non-affine polymers
Kiyosi HORIUTI
|
Abstract
We conduct multi-scale study on energy transfer due to polymers dispersed in homogeneous isotropic turbulence in elasto-inertial regime (EIT). Effect of introduction of non-affinity with macroscopically-imposed deformation in the motion of polymers is examined by connecting mesoscopic Brownian dynamics of elastic dumbbells to macroscopic DNS for solvent. The dumbbells are allowed to be advected either affinely (contravariant) or completely non-affinely (covariant). The relaxation time of polymer is in the order of eddy turnover time. Contravariant polymers drain more energy from the large scales than they can dissipate and transfer the excess energy back into the solvent when they are highly-stretched. It is shown that the skewness of strain-rate tensor in the production term for elastic energy and dissipation rate transfer elastic energy back into the smallest scale of the solvent and increase the dissipation. In the covariant polymers, this backward transfer is eliminated and elastic energy is retained when highly stretched.
Key words
Drag reduction, Polymer, Toms effect, Non-affinity, Dumbbell model, Contravariance, Covariance.
Figures
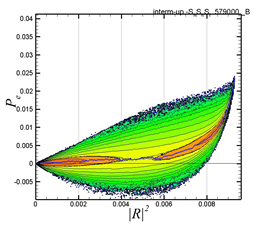
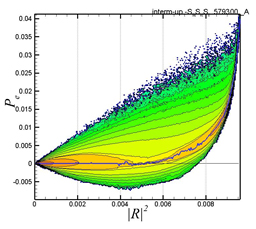
Joint p.d.f. between the dumbbell length |R|2 and the production term for polymer elastic energy, Pe .
Left: obtained from the case using the contravariant dumbbells;
Right: from the case using the covariant dumbbells-


