Newsletter 2022.2 Index
Theme :"The Conference of Fluid Engineering Division (February issue)"
|
Numerical Simulation on Nano Fibril Orientational Control by Electric Field in Cellulose Dispersed Flow
|
Abstract
Cellulose Nano-fibrils (CNFs) are the fundamental building blocks of wood and paid special attentions because of their outstanding mechanical and thermal properties. The mechanical properties of cellulose filament made of CNFs can be improved by their orientation control. In this study, the complex behavior of CNFs in the elongational flow and electric fields were clarified by solving the equation of motion for individual CNFs. Without applied electric field, the CNF orientation degree increases at the flow focusing section by the sheath flow. This is due to the enhanced alignment by the shear and elongation effects. The longer the CNFs are, the higher alignment can be realized in the downstream of the flow focusing section. With electric field applied, shorter CNFs show higher response to the electric field, and the orientation degree increases linearly in the electric field region. In the case of 600 nm, orientation degree was improved by 25.7 % with electric field assisted alignment, although the orientation degree decreases rapidly due to the predominant Brownian rotation in the downstream of electric field region before the sheath injection. The enhancement of CNF alignment by electric field can be shown independent of CNF length. Even for short CNFs, approximately the same orientation degree was obtained as that of longer CNFs without electric field.
Key words
Cellulose nano-fibril, Numerical simulation, Orientation control, Elongational flow, Electric field, flow focusing
Figures
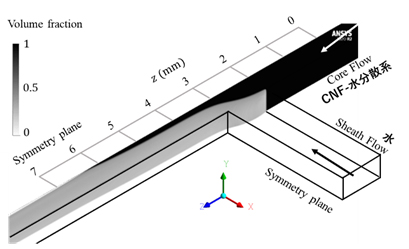
Figure 1 Volume fraction of CNF dispersion in flow-focusing channel.
Movie 1 Visualization of fiber alignment by electric and flow fields (V = 600V, l = 900 nm).
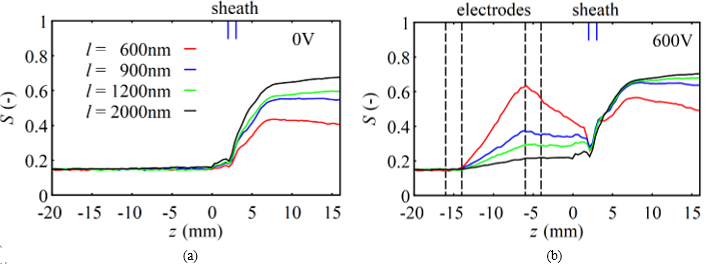
Figure 2 Effect of applied electric field on CNF alignment for (a) V = 0 V and (b) V = 600 V.



