Newsletter 2017.2 Index
Theme : "The Conference of Fluid Engineering Division"
|
The Study of Turbulence in the 21st Century
Shinichiro YANASE
|
Abstract
Turbulence is an eternal target of fluid mechanics. In the end of the 20th century, the numerical simulation of turbulence was started. The famous milestone was Stanford Conference held in 1980-1981. However, the conclusion showed the prematurity of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) mainly due to insufficient computer power. After the conference, a rapid development of the super computer started ironically and CFD of turbulence became popular. But the research is limited in the academic field far from manufacturing industries. In the 21st century, on the other hand, the popularization of turbulence calculation has occurred because of spreading of low coat but high performance PCs and CFD tools in which turbulence models are implemented. Now CFD of turbulence has attained the stage useful even for small manufacturing companies. In this paper, one example of the turbulence calculation using a CFD tool is presented. Turbulence of functional fluids has attracting much interest because of its utility in engineering applications. Among them, turbulence including microbubbles has a lot of physically unique properties and the drag reduction of the pipe flow is observed, which is addressed based on the author’s experimental results. Recently Kolmogorov’s inertial subrange needs reconsideration on its existence condition and ubiquitousness, which needs further study not only theoretically but also experimentally. Finally, the applicability of the probability theory is discussed referring the book of probability and stochastic processes recently written by the author. Though turbulence is probabilistic phenomena, the application of probability theory has not been made much progress these decades. However this way of study is most likely to proceed with advanced technologies of turbulence measurement and advanced mathematics.
Key words
Turbulence, Turbulence Model, Microbubble, Kolmogorov, 21st century
Figures

Fig.1 Q-value representation of the coherentvortices beneath the rotating disk.
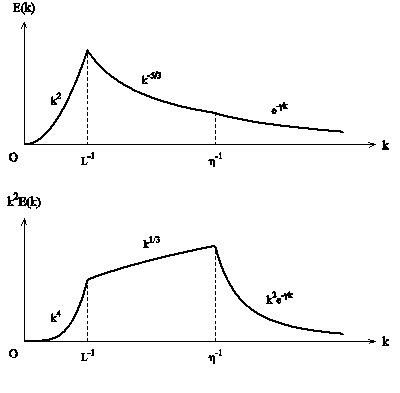
Fig.2 Energy spectrum and enstrophy spectrum
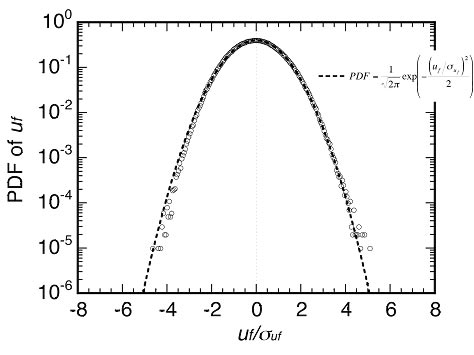
Fig.3 (a) PDF of the velocity field.
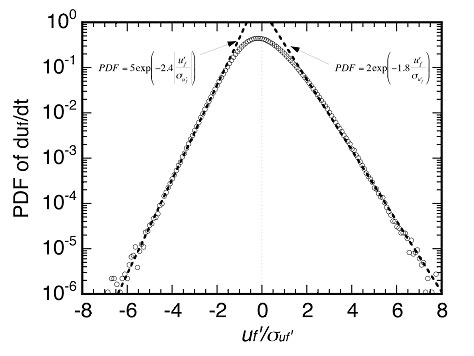
Fig.3 (b) PDF of the time derivative of the velocity field.
References
Batchelor, G. K. , “The Theory of Homogeneous Turbulence”, Cambridge Univ. Press (1953).
Kline, S. J. and Lilley, G. M., Correspondent Report on the Initial Meeting, Held September 3窶・, 1980, of the 1980窶・981
AFOSR-HTTM-Stanford Conference on Complex Turbulent Flows: Comparison of Computation and Experiment, Trans. ASME J. Fluids Eng., 103 (1981), pp.184-188.
Kouchi, T.・熊ukuda, S.・君akano, Y.・郡himizu, Y.・君agata, Y. and Yanase, S.・訓eriodical structure of vortices in a semiconductor single wafer spin cleaner・卦ransactions of the JSME (in Japanese), Vol. 81, No.829 (2015), No.15-00273.
Monin, A. S. and Yaglom, A. M., “Statistical Fluid Mechanics I, II”, M. I. T. Press (1971).
Vassilicos, J. C., Dissipation in Turbulent Flows, Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech., Vol. 47 (2015), pp.95-114.
Yanase, S.・窟FOSR-HTTM-Stanford Conference on Complex Turbulent Flows・沓utsuri・祁ol. 37 (1982), 246-248 (in Japanese).
Yanase, S.・勲atsuura, K.・軍ecent Development of the Micro-bubble Science・君agare・祁ol. 34 (2015), 355-362 (in Japanese).
Yanase, S.・・ldquo;Probability and Stochastic Processes”・勲orikita Pub. Co. (2015) (in Japanese).


