Newsletter 2022.11 Index
Theme : "Mechanical Engineering Congress, 2022 Japan (MECJ-22)”
|
Wall Modelling for Engineering Turbulence CFD
|
Abstract
The essence of the analytical wall-function (AWF) methods for surface boundary conditions of turbulent flows for RANS/LES is briefly summarized. Since the AWF integrates transport equations of momentum and scalars over the control volumes adjacent to surfaces with some simplifications, it is easy to include complex surface-flow physics into the wall-function formula. Hence, the AWF scheme is successful to treat RANS turbulent and scalar transport near solid smooth, rough and permeable walls. High Prandtl or Schmidt number scalar transport near walls or free surfaces are also well handled by the AWF. Its extension to an LES model provides an algebraic non-equilibrium wall-stress model. This article introduces its rationale, fundamental equations and basic procedures with some illustrative application results.
Key words
Analytical wall function, RANS, LES, Engineering CFD
Figures
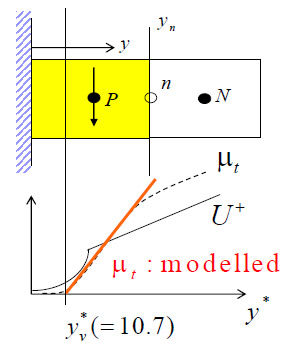
Fig.1 Near-wall cells and simplification of the near-wall eddy viscosity distribution.
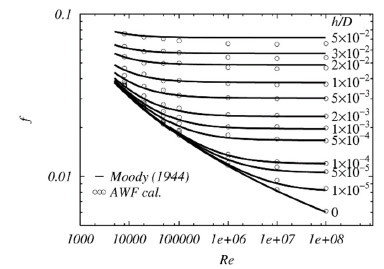
Fig.2 Friction factor of pipe flows depending on roughness height/pope diameter:![]() ( Moody Chart)
( Moody Chart)
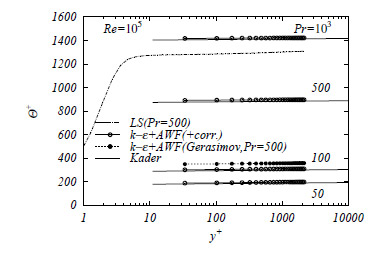
Fig.3 Turbulent thermal fields at high Prandtl number fluids. LS: low Re simulation without WF, Gerasimov: basic AWF, Kader: experimental correlation.
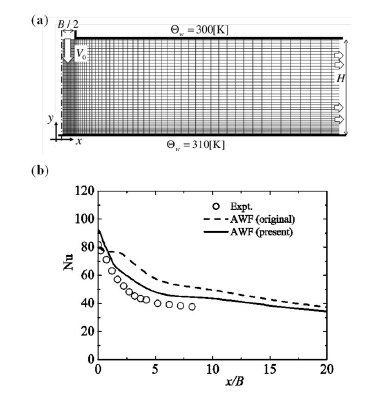
Fig.4 Imping jet heat transfer at Re=20000, H/B=9.2.
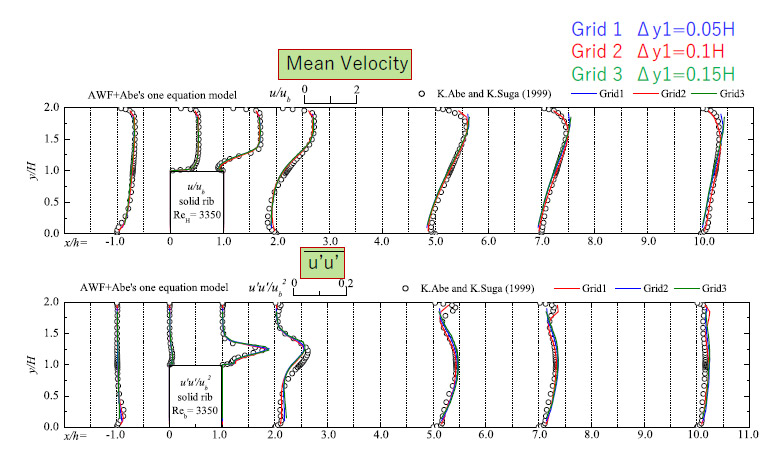
Fig.5 Performance of the AWF-LES in a rib-mounted channel flow.


